We can also get the information of call state using the TelephonyManager class. For this purpose, we need to call the listen method of TelephonyManager class by passing the PhonStateListener instance.
The PhoneStateListener interface must be implemented to get the call state. It provides one method onCallStateChanged().
Android Call State Example
Let's see the example, where we are determining whether phone is ringing or phone is in a call or phone is neither ringing nor in a call.
activity_main.xml
In this example, we don't have any component in this file..
Activity class
Let's write the code to know the call state.
File: MainActivity.java
- package com.javatpoint.callstates;
-
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.telephony.PhoneStateListener;
- import android.telephony.TelephonyManager;
- import android.view.Menu;
- import android.widget.Toast;
-
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
-
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
-
- TelephonyManager telephonyManager =
- (TelephonyManager)getSystemService(Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
-
- PhoneStateListener callStateListener = new PhoneStateListener() {
- public void onCallStateChanged(int state, String incomingNumber)
- {
- if(state==TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_RINGING){
- Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"Phone Is Riging",
- Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
- }
- if(state==TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_OFFHOOK){
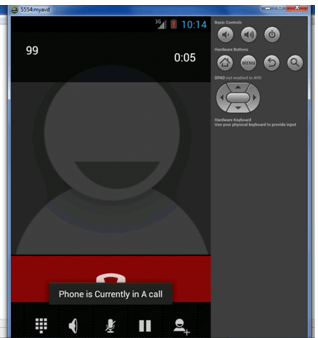
- Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"Phone is Currently in A call",
- Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
- }
-
- if(state==TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_IDLE){
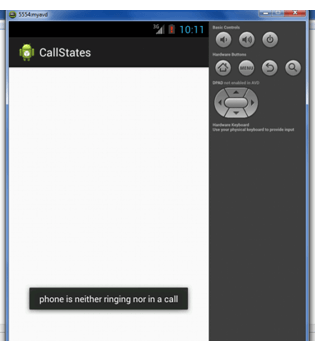
- Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"phone is neither ringing nor in a call",
- Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
- }
- }
- };
- telephonyManager.listen(callStateListener,PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_CALL_STATE);
-
- }
-
- @Override
- public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
-
- getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
- return true;
- }
-
- }
AndroidManifest.xml
You need to provide READ_PHONE_STATE permission in the AndroidManifest.xml file.
File: AndroidManifest.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <manifest xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- package="com.kundan.callstates"
- android:versionCode="1"
- android:versionName="1.0" >
-
- <uses-sdk
- android:minSdkVersion="8"
- android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
-
-
- <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE" />
-
- <application
- android:allowBackup="true"
- android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
- android:label="@string/app_name"
- android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
- <activity
- android:name="com.kundan.callstates.MainActivity"
- android:label="@string/app_name" >
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
-
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
- </application>
-
- </manifest>
Output:


No comments:
Post a Comment