Android recommends to use XMLPullParser to parse the xml file than SAX and DOM because it is fast.
The org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParser interface provides the functionality to parse the XML document using XMLPullParser.
Events of XmlPullParser
The next() method of XMLPullParser moves the cursor pointer to the next event. Generally, we use four constants (works as the event) defined in the XMLPullParser interface.
START_TAG :An XML start tag was read.
TEXT :Text content was read; the text content can be retrieved using the getText() method.
END_TAG : An end tag was read.
END_DOCUMENT :No more events are available
Example of android XMLPullParser
activity_main.xml
Drag the one listview from the pallete. Now the activity_main.xml file will look like this:
File: activity_main.xml
xml document
Create an xml file named employees.xml inside the assets directory of your project.
File: employees.xml
Employee class
Now create the Employee class that corresponds to the xml file.
File: Employee.java
XMLPullParserHandler class
Now write the code to parse the xml file using XMLPullParser. Here, we are returning all the employee in list.
File: XMLPullParserHandler.java
MainActivity class
Now, write the code to display the list data in the ListView.
File: MainActivity.java
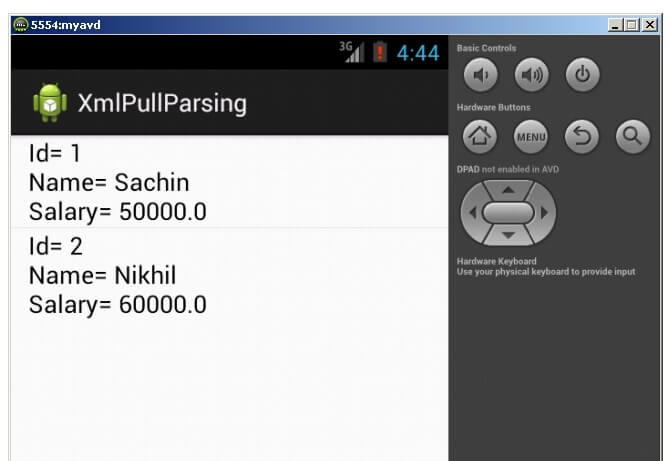
Output:
it is really very important topic and comparatively tough topic
ReplyDelete