Android provides the facility to parse the xml file using SAX, DOM etc. parsers. The SAX parser cannot be used to create the XML file, It can be used to parse the xml file only.
Advantage of SAX Parser over DOM
It consumes less memory than DOM.
Example of android SAX Xml parsing
activity_main.xml
Drag the one textview from the pallete. Now the activity_main.xml file will look like this:
File: activity_main.xml
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- tools:context=".MainActivity" >
-
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/textView1"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
- android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
- android:layout_marginLeft="75dp"
- android:layout_marginTop="46dp"
- android:text="TextView" />
-
- </RelativeLayout>
xml document
Create an xml file named file.xml inside the assets directory of your project.
File: file.xml
- <?xml version="1.0"?>
- <records>
- <employee>
- <name>Sachin Kumar</name>
- <salary>50000</salary>
- </employee>
- <employee>
- <name>Rahul Kumar</name>
- <salary>60000</salary>
- </employee>
- <employee>
- <name>John Mike</name>
- <salary>70000</salary>
- </employee>
- </records>
Activity class
Now write the code to parse the xml using sax parser.
File: MainActivity.java
- package com.javatpoint.saxxmlparsing;
-
-
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParser;
- import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParserFactory;
- import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
- import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
- import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- TextView tv;
- @Override
-
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- tv=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
- try {
- SAXParserFactory factory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
-
- SAXParser saxParser = factory.newSAXParser();
-
-
- DefaultHandler handler = new DefaultHandler() {
-
- boolean name = false;
-
- boolean salary = false;
-
-
- public void startElement(String uri, String localName,String qName,
- Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
- if (qName.equalsIgnoreCase("name"))
- {
- name = true;
- }
- if (qName.equalsIgnoreCase("salary"))
- {
- salary = true;
- }
- }
- public void endElement(String uri, String localName,
- String qName) throws SAXException {
- }
-
- public void characters(char ch[], int start, int length) throws SAXException {
- if (name) {
-
- tv.setText(tv.getText()+"\n\n Name : " + new String(ch, start, length));
- name = false;
- }
- if (salary) {
- tv.setText(tv.getText()+"\n Salary : " + new String(ch, start, length));
- salary = false;
- }
- }
- method
- };
-
- InputStream is = getAssets().open("file.xml");
- saxParser.parse(is, handler);
-
- } catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
- }
- }
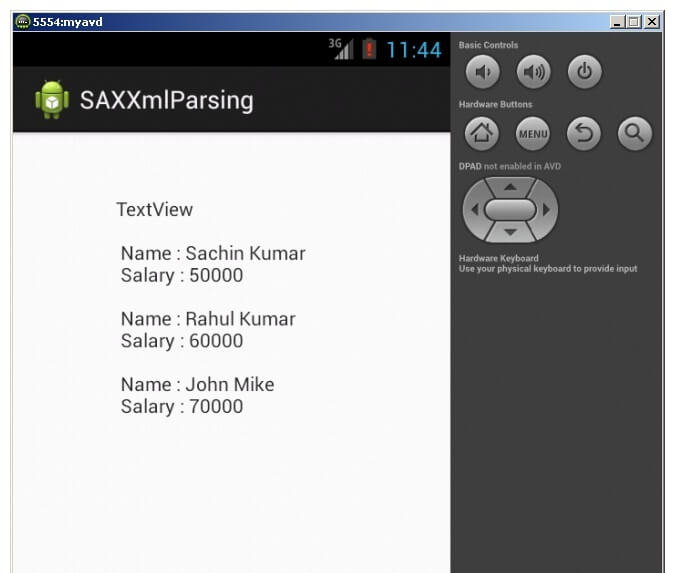
Output:

No comments:
Post a Comment