JSON (Javascript Object Notation) is a programming language . It is minimal, textual, and a subset of JavaScript. It is an alternative to XML.
Android provides support to parse the JSON object and array.
Advantage of JSON over XML
1) JSON is faster and easier than xml for AJAX applications.
2) Unlike XML, it is shorter and quicker to read and write.
3) It uses array.
json object
A JSON object contains key/value pairs like map. The keys are strings and the values are the JSON types. Keys and values are separated by comma. The { (curly brace) represents the json object.
- {
- "employee": {
- "name": "sachin",
- "salary": 56000,
- "married": true
- }
- }
json array
The [ (square bracket) represents the json array.
- ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"]
Let's take another example of json array.
- { "Employee" :
- [
- {"id":"101","name":"Sonoo Jaiswal","salary":"50000"},
- {"id":"102","name":"Vimal Jaiswal","salary":"60000"}
- ]
- }
Example of android JSON parsing
activity_main.xml
Drag the one textview from the pallete. Now the activity_main.xml file will look like this:
File: activity_main.xml
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- tools:context=".MainActivity" >
-
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/textView1"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
- android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
- android:layout_marginLeft="75dp"
- android:layout_marginTop="46dp"
- android:text="TextView" />
-
- </RelativeLayout>
Activity class
Let's write the code to parse the xml using dom parser.
File: MainActivity.java
- package com.javatpoint.jsonparsing;
-
- import org.json.JSONException;
- import org.json.JSONObject;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.widget.TextView;
-
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- public static final String JSON_STRING="{\"employee\":{\"name\":\"Sachin\",\"salary\":56000}}";
-
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
-
- TextView textView1=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
-
- try{
- JSONObject emp=(new JSONObject(JSON_STRING)).getJSONObject("employee");
- String empname=emp.getString("name");
- int empsalary=emp.getInt("salary");
-
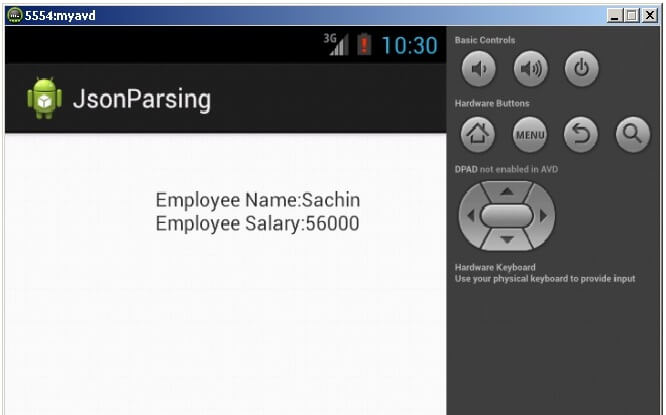
- String str="Employee Name:"+empname+"\n"+"Employee Salary:"+empsalary;
- textView1.setText(str);
-
- }catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
-
- }
-
- }
Output:
Parsing JSONArray in Android
By the help of JSONArray class, you can parse the JSONArray containing the JSON Objects. Let's see the simple example to parse the json array.
File: MainActivity.java
- package com.example.jsonparsing2;
-
- import org.json.JSONArray;
- import org.json.JSONException;
- import org.json.JSONObject;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.widget.TextView;
-
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
-
- TextView output = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
-
- String strJson="{ \"Employee\" :[{\"id\":\"101\",\"name\":\"Sonoo Jaiswal\",\"salary\":\"50000\"},{\"id\":\"102\",\"name\":\"Vimal Jaiswal\",\"salary\":\"60000\"}] }";
-
- String data = "";
- try {
-
- JSONObject jsonRootObject = new JSONObject(strJson);
-
-
- JSONArray jsonArray = jsonRootObject.optJSONArray("Employee");
-
-
- for(int i=0; i < jsonArray.length(); i++){
- JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
-
- int id = Integer.parseInt(jsonObject.optString("id").toString());
- String name = jsonObject.optString("name").toString();
- float salary = Float.parseFloat(jsonObject.optString("salary").toString());
-
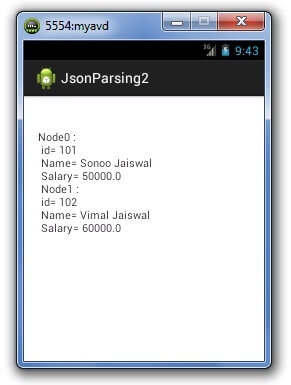
- data += "Node"+i+" : \n id= "+ id +" \n Name= "+ name +" \n Salary= "+ salary +" \n ";
- }
- output.setText(data);
- } catch (JSONException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
- }
- }
Output:


my teacher says that this topic is most important in company.
ReplyDeletekundan, you explained it very well
But i am also looking for a rich content of this topic